CPPF: Towards Robust Category-Level 9D Pose Estimation in the Wild
Yang You, Ruoxi Shi, Weiming Wang, Cewu Lu
CVPR 2022


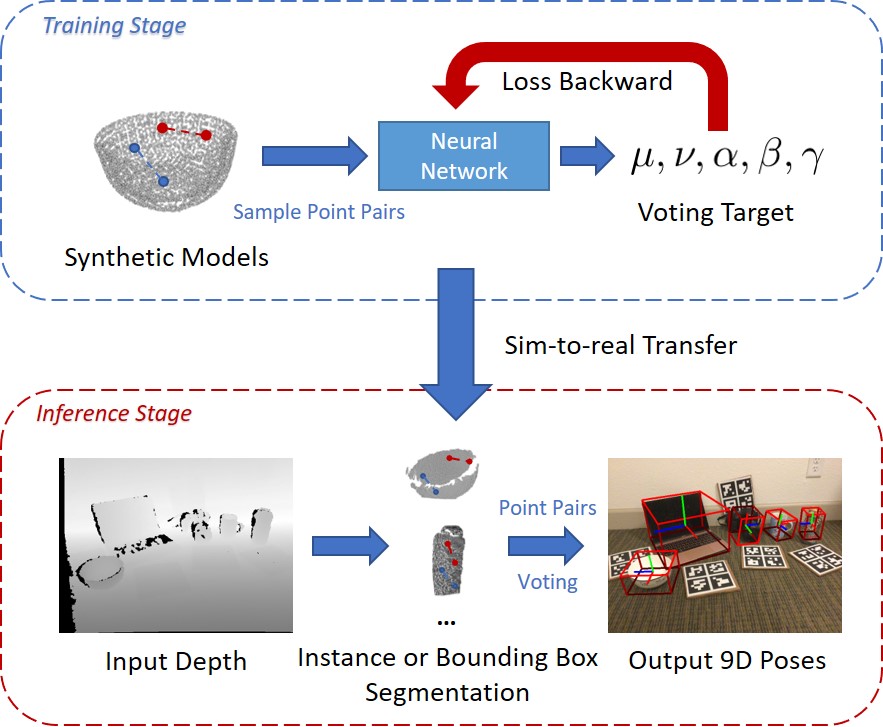
CPPF is a pure sim-to-real method that achieves 9D pose estimation in the wild. Our model is trained solely on ShapeNet synthetic models (without any real-world background pasting), and could be directly applied to real-world scenarios (i.e., NOCS REAL275, SUN RGB-D, etc.). CPPF achieves the goal by using only local $SE3$-invariant geometric features, and leverages a bottom-up voting scheme, which is quite different from previous end-to-end learning methods. Our model is robust to noise, and can obtain decent predictions even if only bounding box masks are provided.
Abstract
In this paper, we tackle the problem of category-level 9D pose estimation in the wild, given a single RGB-D frame. Using supervised data of real-world 9D poses is tedious and erroneous, and also fails to generalize to unseen scenarios. Besides, category-level pose estimation requires a method to be able to generalize to unseen objects at test time, which is also challenging. Drawing inspirations from traditional point pair features (PPFs), in this paper, we design a novel Category-level PPF (CPPF) voting method to achieve accurate, robust and generalizable 9D pose estimation in the wild. To obtain robust pose estimation, we sample numerous point pairs on an object, and for each pair our model predicts necessary SE(3)-invariant voting statistics on object centers, orientations and scales. A novel coarse-to-fine voting algorithm is proposed to eliminate noisy point pair samples and generate final predictions from the population. To get rid of false positives in the orientation voting process, an auxiliary binary disambiguating classification task is introduced for each sampled point pair. In order to detect objects in the wild, we carefully design our sim-to-real pipeline by training on synthetic point clouds only, unless objects have ambiguous poses in geometry. Under this circumstance, color information is leveraged to disambiguate these poses. Results on standard benchmarks show that our method is on par with current state of the arts with real-world training data. Extensive experiments further show that our method is robust to noise and gives promising results under extremely challenging scenarios.
Method Overview
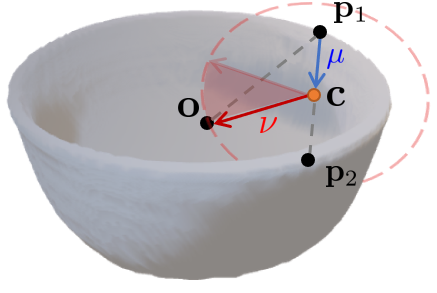
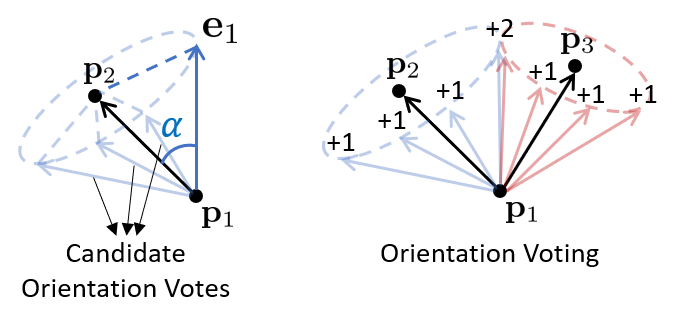
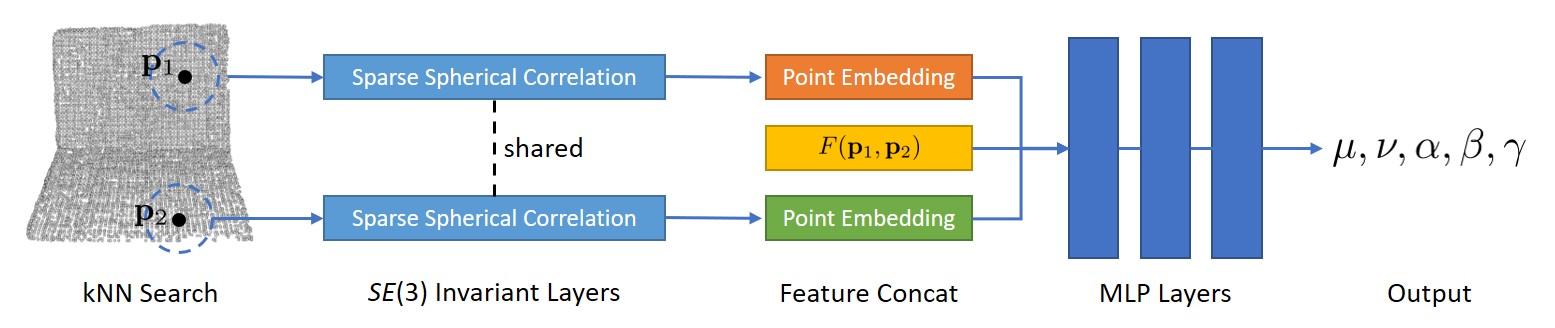
For each sampled point pair lying on an object, we generate both center votes and orientation votes as illustrated above; while votes for scales are the average of predicted scales for all pairs. The network architecture predicting these voting targets are illustrated below:
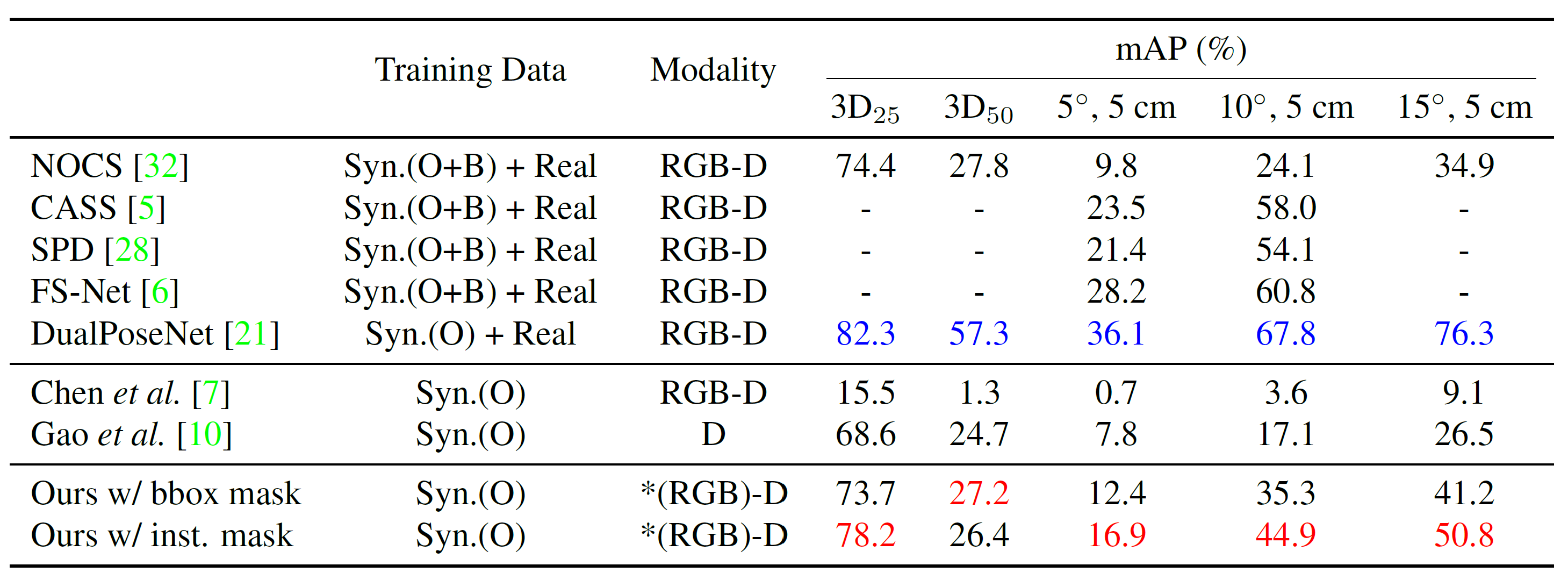
Quantitative Results
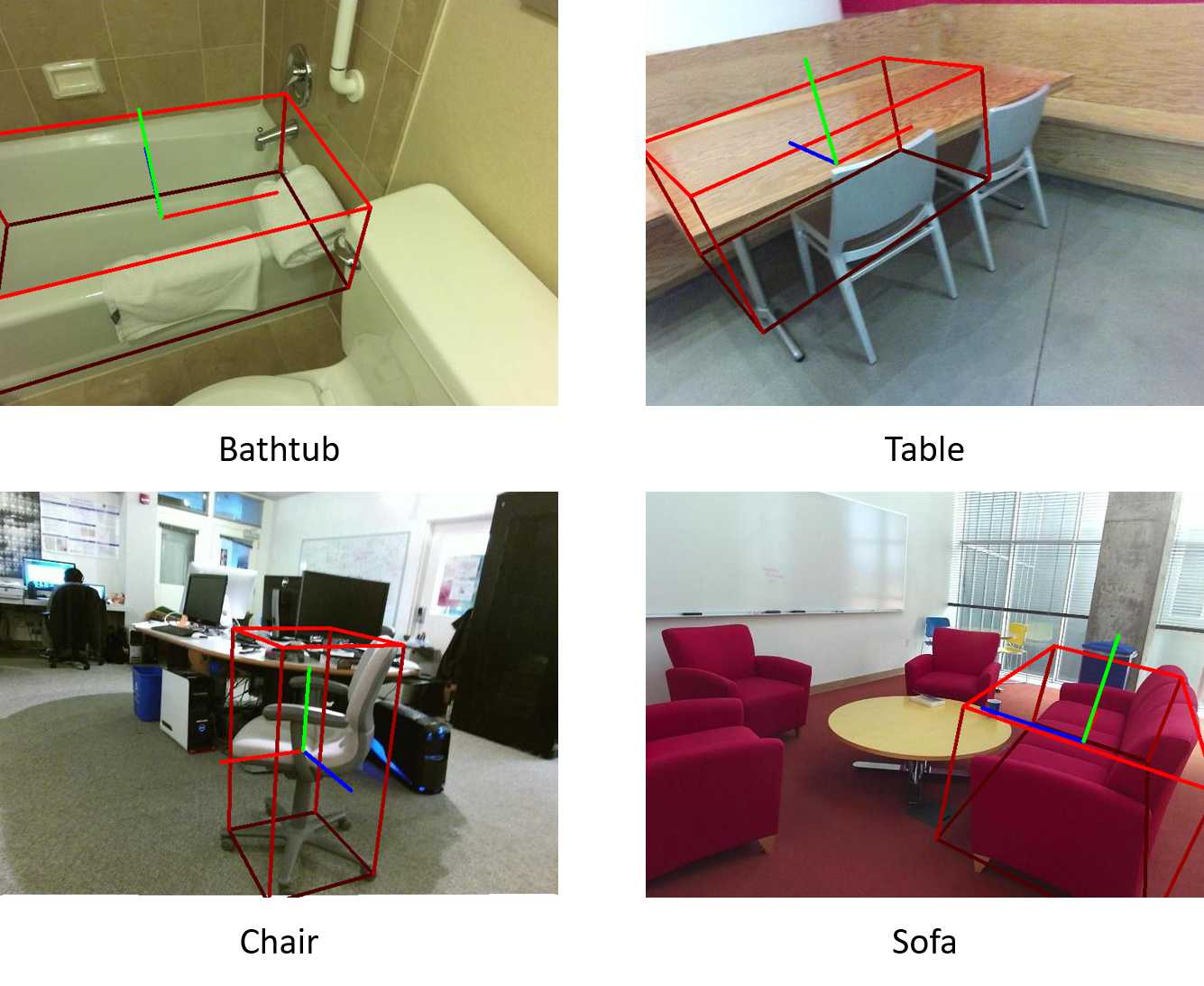
Qualitative Results
NOCS REAL275 with Instance Segmentation Masks

NOCS REAL275 with Bounding Box Masks

SUN RGB-D in the Wild

Citation
@inproceedings{you2022cppf,
title={CPPF: Towards Robust Category-Level 9D Pose Estimation in the Wild},
author={You, Yang and Shi, Ruoxi and Wang, Weiming and Lu, Cewu},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
year={2022}
}